What Is Dry Batch Concrete Batching Plant
Ready-mixed concrete is produced following specific procedures at batching facilities and then delivered to construction sites by mixer trucks.
Types of Concrete Batching Plants and Their Production Procedures
Concrete batching plants can be categorized mainly into two types, with four combinations based on their production procedures:
- Dry batch concrete plant
- Wet batch concrete plant
- Half-wet batch concrete plant
- Combination batch concrete plant
Choosing the appropriate concrete batching plant depends on the construction characteristics and the available transportation facilities. The primary difference between dry mixed concrete plants and wet mixed concrete plants is not just the moisture content but also other significant operational differences.
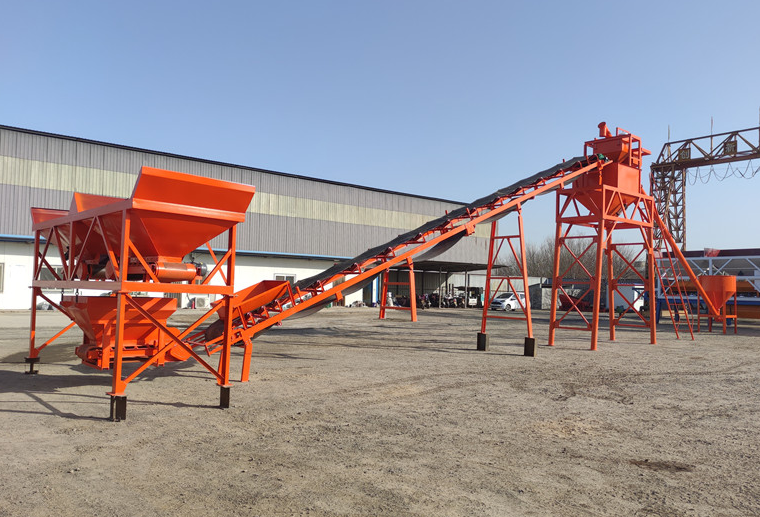
A dry batch concrete plant is specifically designed to mix concrete more efficiently than other batching plants. It requires the use of a mixer truck to complete the mixing process, offering higher efficiency in concrete production.
A dry batch concrete plant combines aggregate materials such as sand, gravel, and cement in precise measurements. The mixture is discharged into a mixer truck, combined with a measured amount of water, and mixed in the truck on the way to the site.
A wet batch plant, on the other hand, mixes all components (including water) at a central location. The mixture is continuously stirred during transport to the site to prevent setting, using agitators or pre-mixed trucks.
Components and Operation of a Dry Batch Concrete Batching Plant
Similar to mobile and stationary batching plants, a dry batch plant consists of several key components:
- Cement Silos: Store raw materials such as cement, sand, and fly ash.
- Feeding System: Connects aggregates to the mixing system.
- Control System: The core of the plant, enabling full automation from the control room.
- Weighing System: Determines the quantity of mixed materials, influencing the quality of the concrete.
- Mixing System: Mixes materials without water; the mixer truck is crucial for transporting and mixing.
Differences Between Dry and Wet Mixing Equipment
Dry mixing plants differ from wet mixing plants primarily in their mixing process. A wet mix plant has a central mixer, while a dry mix plant does not. The dry mix method can provide a more consistent mixture in a shorter period. However, dry batching plants usually experience more variations in the standard deviation of breaking strength and changes from load to load, as the mixing of cement, stone, and other materials can be less systematic than in wet mixing. Some plants combine both dry and wet mix characteristics to enhance application versatility.
Advantages of Dry Concrete Batching Plants
- Higher Capacity and Lower Energy Consumption: Dry batching plants can mix materials without water, leading to increased capacity and reduced energy usage.
- Increased Productivity and Time Savings: The cooperation between the dry batching plant and the mixer truck boosts productivity and saves time.
- Fresh Concrete at the Construction Site: Mixer trucks deliver fresh concrete directly to the site, ensuring high-quality material.
- Enhanced Construction Efficiency: Dry batching plants shorten construction times and enhance overall productivity.
- Lower Power Consumption: Compared to wet mix plants, dry batching plants consume less power.
- Lower Operating Costs: The operating costs of dry-batch plants are relatively low.
- Efficient Mixing: Dry batching allows for more efficient mixing of concrete.
- Reduced Maintenance Time: Dry mix plants require less maintenance compared to wet mix plants.
- Automation: Like other mixing plants, such as mobile and stationary plants, dry batching plants are also automated.
- Ideal for Long Sites: If the construction site is extensive, dry batching plants are ideal. The mixer truck can maintain rotation to prevent the concrete from tampering or hardening, ensuring the freshness of the material.
- Modern Construction Aid: Dry batch plants are highly valued modern production equipment that significantly contributes to the development and construction of modern roads, bridges, and various construction projects.