Belt Type Concrete Batching Plant: All You Need To Know
The belt type concrete batching plant is a widely used piece of equipment in the construction industry. Known for its irreplaceable advantages, this type of plant is favored in various modern construction projects. It remains one of the most trusted choices for investors and project managers alike.
So, what makes it special? Let's explore the features and benefits of the belt type concrete batching plant.
What is a Belt Type Concrete Batching Plant?
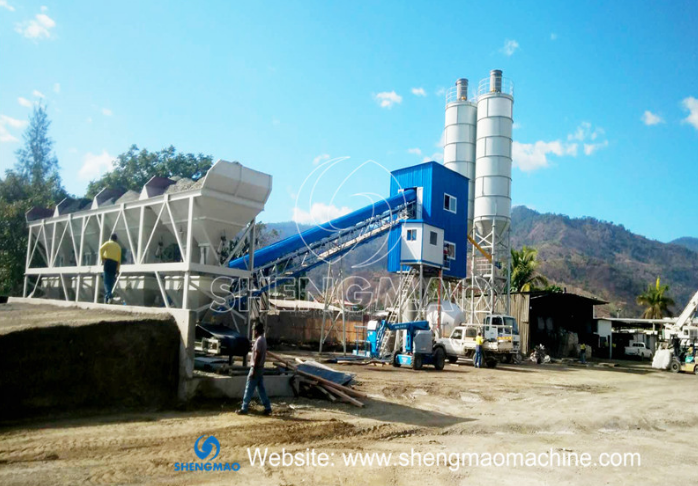
A belt type concrete batching plant is named after the belt conveyor system used within it. This conveyor is typically positioned under the aggregate batching machine to transport the measured materials to the main mixer. Another conveyor system, called the hopper hoist, is also used in some configurations (detailed in the following paragraph).
The belt type concrete batching plant is a specialized type of plant that feeds, measures, and mixes various materials—such as different sizes of stones, sand, cement, fly ash, water, and additives—to create various concrete mixtures tailored to specific construction needs.
This type of batching plant is widely utilized in the modern construction industry, particularly in large and medium-sized projects with substantial engineering demands and extended construction periods. Typical applications include water conservancy projects, hydropower facilities, bridges, airports, ports, and other infrastructure developments.
Main Configurations of a Belt Type Concrete Batching Plant
Belt Feeding Conveyor: Efficiently and continuously delivers aggregates.
Aggregate Batching Machine: Features a separate weighing system that automatically ensures the accurate proportioning of each aggregate component.
Weighing System: Equipped with precise load cells for cement, water, and additives, ensuring weighing accuracy within ±1%.
Pneumatic System: Controlled automatically by a PLC and computer system, providing convenient and stable operation. It can also be switched to manual mode if necessary.
Main Frame Support: Composed of a sturdy steel structure for stability.
Bolt Type Cement Silo: Easy to disassemble and transport, offering durability and reliability.
Cement Screw Conveyor: Includes a full sealing device, with a soft connection between the discharge port and measuring bucket to maintain measurement accuracy.
Full-Automatic Control System: Features a control room with air conditioning, ensuring a safe and stable control environment.
Types of Concrete Batching Plants
In addition to belt type concrete batching plants, there are several other types commonly used on construction sites. They can be classified according to different criteria:
Dry or Wet Concrete Batching Plant: Based on the type of concrete produced.
Stationary or Mobile Concrete Mixing Plant: Based on mobility.
Commercial or Project Concrete Batching Plant: Based on the intended use.
Belt or Hopper Type Concrete Mixing Plant: Based on the feeding method.
Other classification methods may also exist. Each type of batching plant is designed and manufactured to meet specific construction needs. The goal is to provide efficient and reliable concrete mixing solutions that enhance project speed and quality, contributing to modern construction's demands for speed, quality, and strength.
Advantages of Belt Type Concrete Batching Plants
Belt type concrete batching plants offer several advantages over hopper type plants, thanks to their flexible and stable belt conveyor systems. Some of the key benefits include:
Large Loading Capacity: The belt conveyor can handle a large volume of aggregates, providing stable and reliable operation. This makes it ideal for construction projects requiring a significant amount of concrete.
Modular Structure Design: The plant's modular structure allows for easy installation and transportation, reducing costs associated with logistics.
Accurate Material Weighing Systems: The separated weighing systems ensure precise proportions of all mixing materials, adhering strictly to the ingredient specifications.
Low Energy Consumption: The design minimizes energy use, leading to lower production costs.
Adaptability and Flexibility: The belt conveying system can be easily adapted and installed in narrow or complex environments, such as small tunnels.
Dust Control: Equipped with a dust collector, the plant efficiently reduces airborne dust, contributing to a cleaner working environment.
Belt Conveyor in Concrete Batching Plants
The belt conveyor is an essential and economical component in concrete batching plants for transporting aggregates. It typically includes a sweeper, driving device, frame, hanging idler, parallel lower idler, diverting roller, tension device, hood, maintenance walkway, belt, hopper, adjusting screw, and emergency stop switch, among other parts.
Tension Device: Ensures the conveyor belt has sufficient tension, providing the necessary friction between the belt and the drive roller to prevent slipping. It also allows for length adjustment of the belt.
Hood: Serves as a dust-proof and rainproof cover.
Idler: Supports the conveyor belt and the materials on it, ensuring smooth operation.
Adjusting Screw: Used to tension the conveyor belt and adjust its running state, ensuring it remains in the correct position.
Redirecting Roller: Changes the running direction of the conveyor belt or increases the wrapping angle between the belt and the drive roller.
The conveyor belt itself is a continuous loop, wrapped around the drive roller and the redirecting roller at the tail. Numerous idlers support the belt along its length. Material is fed onto the belt by a charging device at one end and unloaded at the other by various unloading devices, typically located at the end of the conveyor.
In aggregate production and transportation, the unloading usually occurs at the conveyor's end. The drive roller, powered by a motor via a reducer, moves the conveyor belt in a circular motion through friction.
An inclined belt conveyor is designed to move aggregates upward to the mixing system. The inclination angle of the belt conveyor should generally not exceed 30 degrees to ensure efficient material transport.
How Does a Belt Type Concrete Batching Plant Work?
A belt conveyor concrete batching plant operates through five main steps: materials feeding, weighing, conveying, mixing, and unloading.
Materials Feeding: Aggregates are loaded into the batching machine using a loader. They are then transferred into the weighing hoppers after a brief pause.
Weighing: The weighed aggregates are conveyed by the belt conveyor to the mixer, where other pre-weighed materials are also added.
Conveying: The powder components are conveyed by a powder screw conveyor, while water and additives are pumped directly into the measuring system and then into the mixer.
Mixing: Inside the central mixing machine, twin shafts mix all the materials. The mixture is lifted and dropped by gravity, ensuring thorough and even mixing.
Unloading: In a short period (approximately 60 seconds), the finished concrete mixture is unloaded, completing the batching process for that batch of concrete.
What About Hopper Concrete Batching Plants?
Hopper type and belt type concrete batching plants are two distinct types of stationary concrete batching plants.
Firstly, the primary difference between them lies in their aggregate conveying methods. The belt type uses a belt conveyor system, while the hopper type employs a skip hopper lifting mechanism.
Secondly, belt type concrete batching plants offer higher conveying capacity and output, making them ideal for large and medium-sized construction projects. In contrast, hopper type plants are better suited for smaller projects due to their lower conveying capacity, limited by the hopper size and footprint.
Thirdly, belt type plants typically feature a waiting silo, with the main machine and belt enclosed. They often use independent weighing for batching. On the other hand, hopper type plants generally do not have a waiting silo; they use cumulative weighing for batching and have a simpler structure.
Finally, hopper type plants are generally more cost-effective due to their simpler design and construction.